In this Huge world, 90% of work is digitalized. To maintain all this data, large amounts of electronic devices are required and for these devices, a large amount of semiconductor material is needed.
There are many Semiconductor materials but Silicon is the most suitable element.
what is semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material between the conductor and the insulator properties. This property helps to control the electricity flow inside electronic chips or processors.
- Examples- Mobile, smartwatches, vehicles, electronic vehicles, and many more electronic devices
Important Properties:
- Semiconductor element has less conductive properties of electricity than conductors and lesser insulation properties than an insulator.
- Semiconductor conductivity increases as temperature increases and vice versa.
- It acts as an insulator at zero degrees Kelvin and acts as a conductor as temperature increases.
- It is suitable for high temperatures and it maintains its working condition
- It has also high dielectric properties which means it can withstand high electric fields without breaking down.
Why do Electronics devices need semiconductor elements rather than Metal elements?
Metal like copper is a good conductor of electricity but electricity flow can not be controlled here. This is because metals’ insulation properties are nearly zero.
But in the case of semiconductors, it has both properties like insulation and conduction of electricity. This property helps the semiconductor control the electricity flow inside a Processor of the electronic device.
By doping (adding impurities) the semiconductor, we can increase the conductivity.
How many semiconductors are there in the periodic table?
In the Periodic table semiconductors are located in groups 13-16 including Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic, Antimony, and Tellurium, and some elements are Cadmium and zinc which are located in group 12. By adding impurities in Cd and Zn they act as semiconductors.
Why is silicon used in an electronic device?
On Earth 27.7 % of The Earth’s crust is Silicon. Mostly silicon is extracted from sand which is easy to available for production.
These 3 factors help an engineer to decide a martial for production
- Availability- How much is available in the world
- processing cost must be low
- Is this material efficient for the final product?
what are The Properties Of silicon?
- Easily available, you can extract it from the sand.
- Its atomic structure helps while adding impurities it acts as a P-Type and N-Type semiconductor. This will help in controlling the electricity flow.
- At high-temperature conditions, it works well.
All the mobile, laptop, and smartwatch processors are made of Silicon wafers. Silicon is also used to produce Engine blocks, here silicon is added as an impurity.
Atomic structure of Silicon
Silicon has a property that while adding impurities can act as a good conductor of electricity. It is because
The atomic number of silicon in the periodic table is 14 and it has 4 electrons in the valance shell.
If we add Pentavalent atoms like phosphorus which has 5 electrons in the valance shell. Extra electron helps to increase the conductivity.
In Electronic configuration of Si is 1S2, 2S2, 2P6, 3S2, 3P2.
- 1st subshell i.e. 1S2 has 2 electrons
- 2nd subshell i.e. 2S2and 2P6 has 8 electrons
- 3rd subshell blue in color occupies 8 electrons but in the case of silicon, there are 4 electrons.
- These valence electrons participate in chemical bonding with other atoms to form compounds.
How silicon is extracted from Sand?
There are several methods let’s see which method is most effective and cost-effective.

Metallaurgical Silicon
In this process source material is Quartz. it is the rock form of the purest silicon oxide.
During this process, In a closed system, there are two electrodes. while applying electricity heat is generated and melts the Quartz.

Temperature is raised to 1900 degree celsius inside the furnace because the Si melting temperature is around 1400 degrees Celsius.
Molten Silicon Oxide in the presence of carbon reacts with each other and molten Silicon is separated from the furnace and oxygen is released in the form of Carbon monoxide.
Here the purity of Silicon is about 98 to 99 percent. This process is mainly used in the Aluminum Casting industry which makes Automotive Engine blocks.
Polysilicon
This process is also known as Siemens Process. In this process source material is Metallurgical Silicon in powder form.
This metallurgical silicon was exposed in a reactor with HCL at an elevated temperature in the presence of a catalyst.
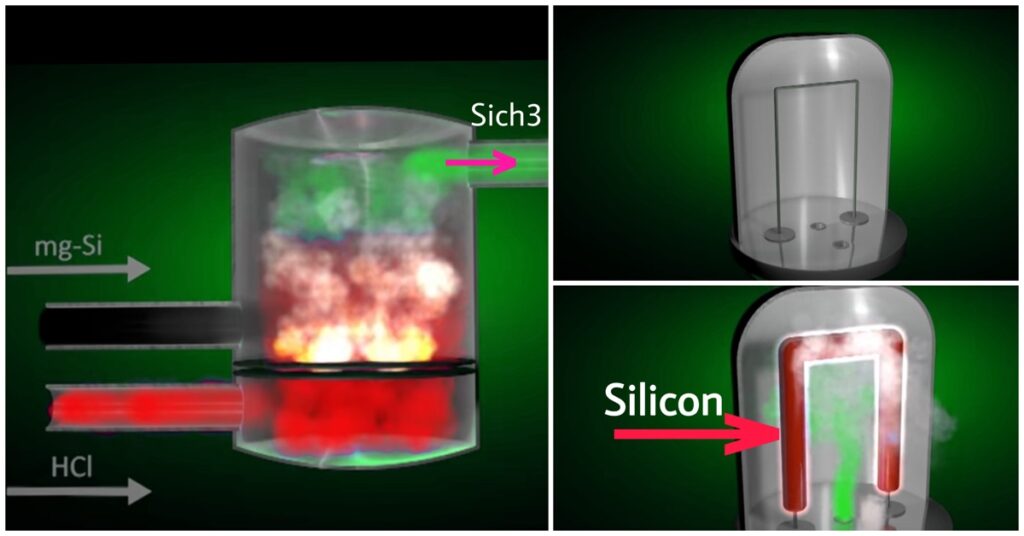
The gas is cooled at high and low temperatures and moved with distillation. Here the temperature is about 850 to 1000 degrees Celsius.
Again SiHcl3 is vapourised inside a reactor and 3 outcomes came to Si, Cl, and hydrogen. Here cl and H are in a gaseous state and Si will deposit along the rod inside the reactor.
All these Cl and H gases are purified and hydrogen gas is again used in the reactor.
Polycrystalline silicon
This process is also known as Czochralski Method. This method is so less cost-effective because it consumes less energy. This is the important reason why most manufacturers use this method to produce silicon wafers for the semiconductor chip.
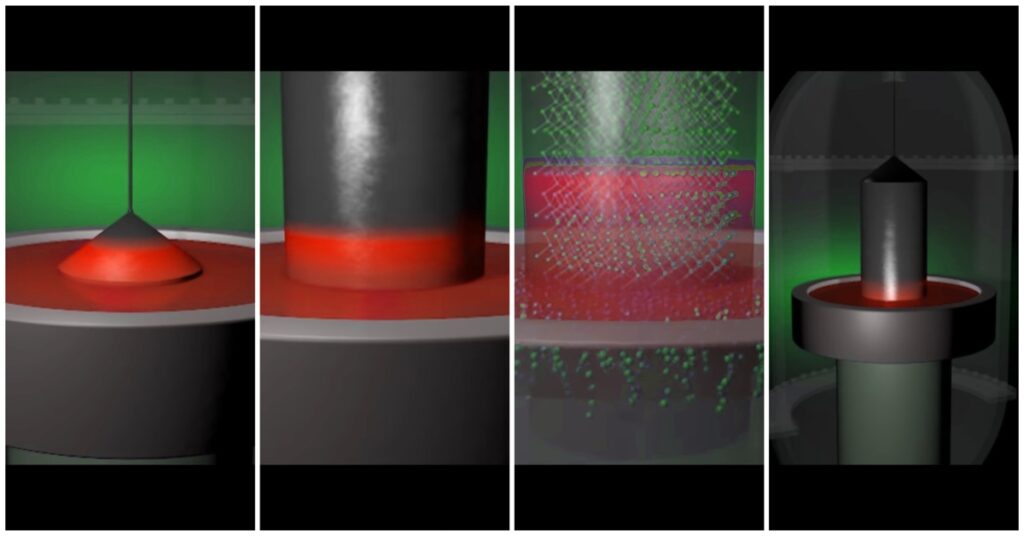
It is the purest form of Silicon about 99.999%. In this process, a furnace is required where the temperature is about 1500 degree Celsius. This process is done under an inert gas atmosphere like Argon gas.
A silicon seed rotates around itself by a rotor with a specific speed. When the silicon seed is deep inside the molten material all crystalline silicon material started sticking to this silicon seed.
In this process, the semiconductor manufacturers extract the purest form of Silicon from the sand.
conclusion
The Silicon manufacturing industry is rapidly increasing due to a large number of electronic devices. A Taiwan industry TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) is one of the largest manufacturers of semiconductors. Among processes which process is your favorite process comment below.
This research definitely improves your prospect regarding how semiconductor chip is made.